Electron Capture Detector (ECD)
In stock
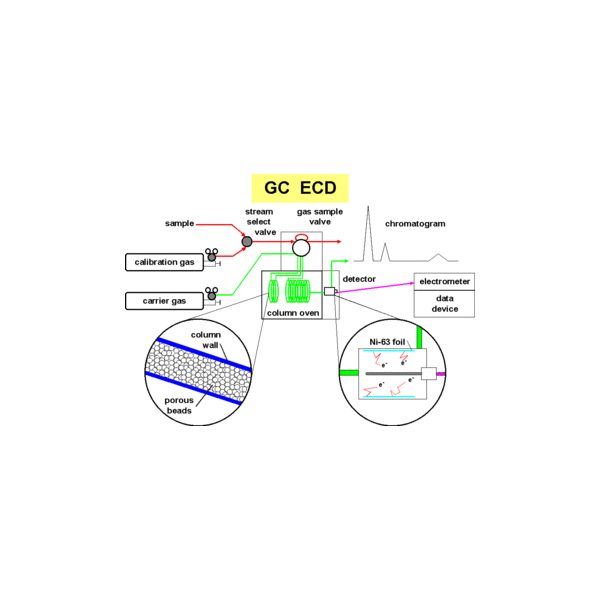
The electron capture detector is used for detecting electron-absorbing components (high electronegativity) such as halogenated compounds in the output stream of a gas chromatograph. The ECD uses a radioactive beta particle (electron) emitter in conjunction with a so-called makeup gas flowing through the detector chamber. The electron emitter typically consists of a metal foil holding 10 millicuries (370 MBq) of the radionuclide 63
Ni
. Usually, nitrogen is used as makeup gas, because it exhibits a low excitation energy, so it is easy to remove an electron from a nitrogen molecule. The electrons emitted from the electron emitter collide with the molecules of the makeup gas, resulting in many more free electrons. The electrons are accelerated towards a positively charged anode, generating a current. There is therefore always a background signal present in the chromatogram. As the sample is carried into the detector by the carrier gas, electron-absorbing analyte molecules capture electrons and thereby reduce the current between the collector anode and a cathode. Over a wide range of concentrations the rate of electron capture is proportional to the analyte concentration. ECD detectors are particularly sensitive to halogens, organometallic compounds, nitriles, or nitro compounds.
In stock
Enquiry about Electron Capture Detector (ECD)